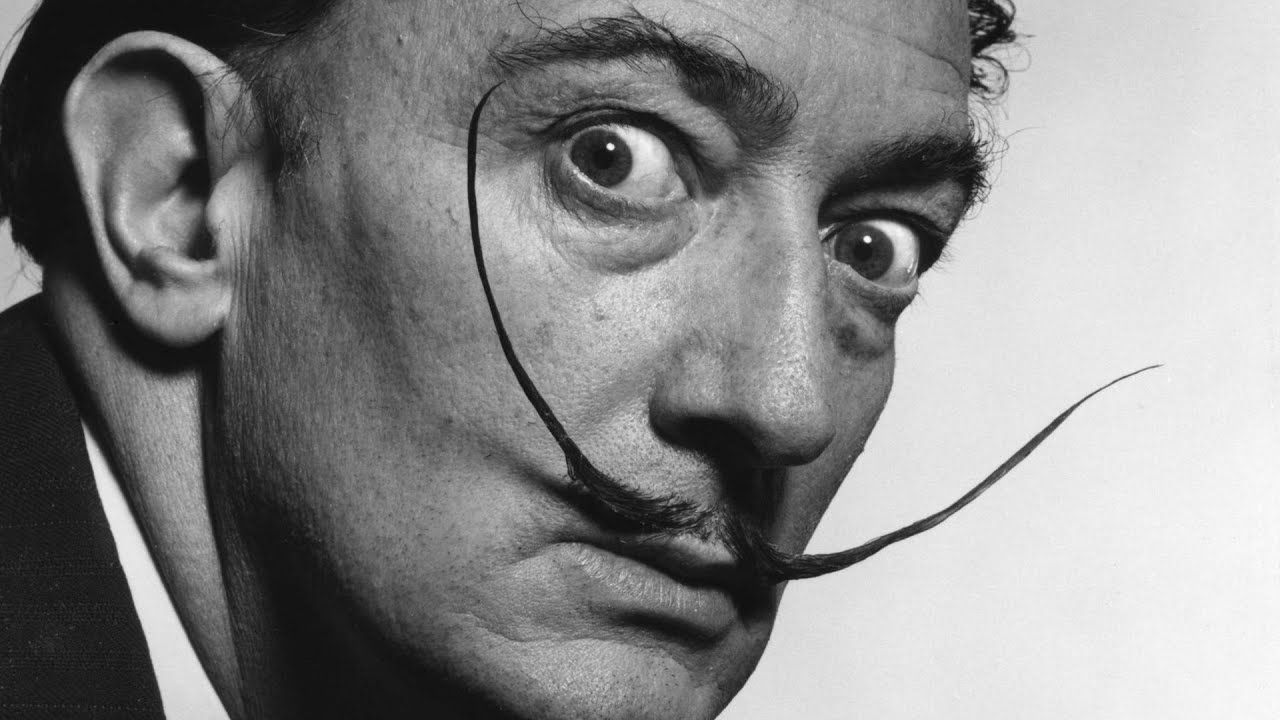
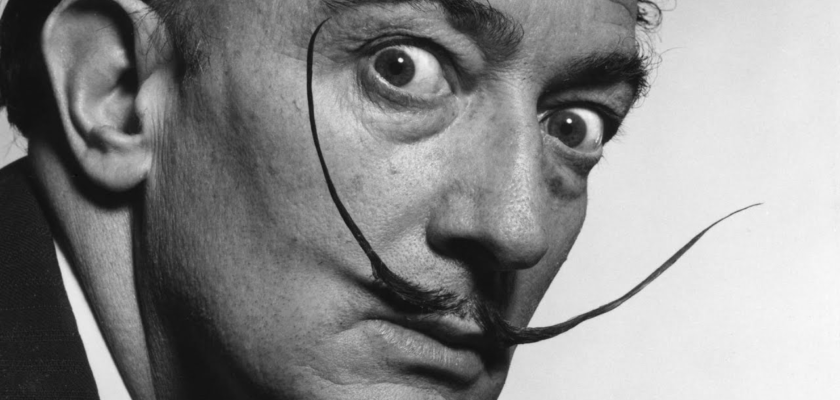
Salvador Dalí in full Salvador Domingo Felipe Jacinto Dalí i Domènech, Marquess of Dalí of Púbol was a Spanish surrealist artist. He was renowned for his technical skill, precise draftsmanship, and the striking and bizarre images in his work.
Dalí’s life-long interest in science and mathematics was often reflected in his work. His soft watches have been interpreted as references to Einstein’s theory of the relativity of time and space. Images of atomic particles appeared in his work soon after the atomic bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki and strands of D.N.A. appeared from the mid-1950s. In 1958 he wrote in his Anti-Matter Manifesto: “In the Surrealist period, I wanted to create the iconography of the interior world and the world of the marvelous, of my father Freud.
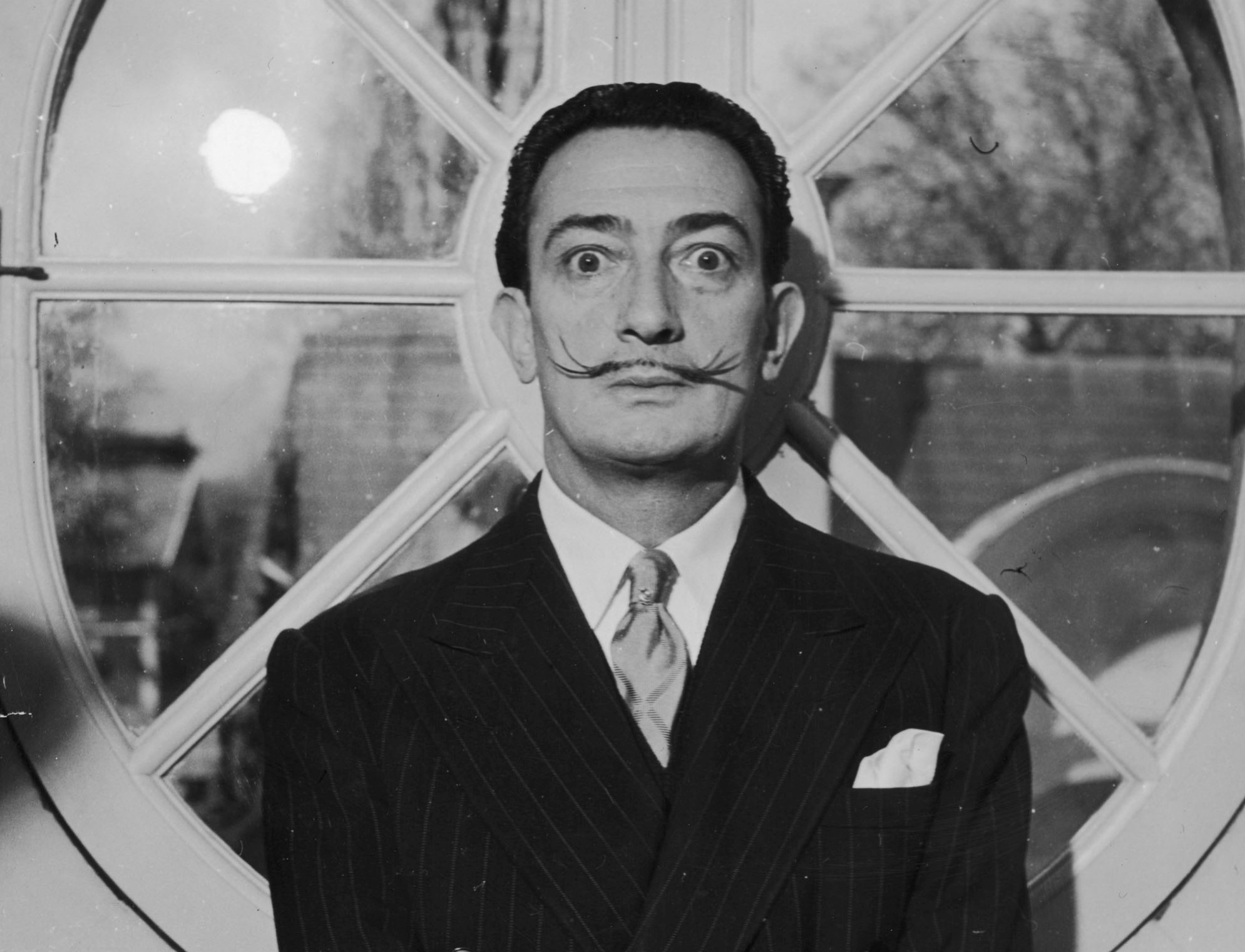

As an art student in Madrid and Barcelona, Dalí assimilated a vast number of artistic styles and displayed unusual technical facility as a painter. It was not until the late 1920s, however, that two events brought about the development of his mature artistic style: his discovery of Sigmund Freud’s writings on the erotic significance of subconscious imagery and his affiliation with the Paris Surrealists, a group of artists and writers who sought to establish the “greater reality” of the human subconscious over reason. To bring up images from his subconscious mind, Dalí began to induce hallucinatory states in himself by a process he described as “paranoiac critical.”
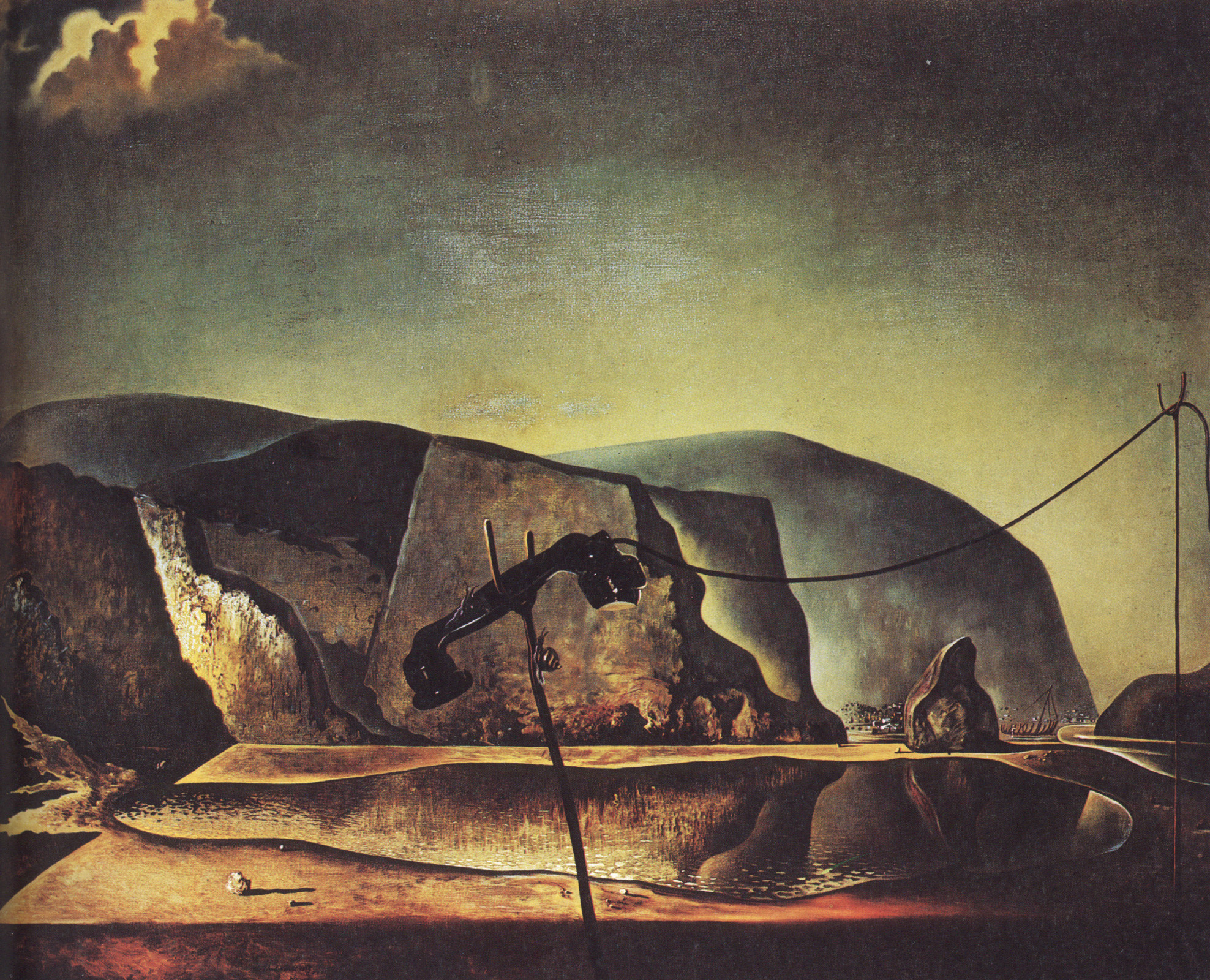

The rhinoceros and rhinoceros horn shapes began to proliferate in Dalí’s work from the mid-1950s. According to Dalí, the rhinoceros horn signifies divine geometry because it grows in a logarithmic spiral. He linked the rhinoceros to themes of chastity and to the Virgin Mary. However, he also used it as an obvious phallic symbol as in Young Virgin Auto-Sodomized by the Horns of Her Own Chastity.

Food and eating have a central place in Dalí’s thoughts and work. He associated food with beauty and sex and was obsessed with the image of the female praying mantis eating her mate after copulation. Bread was a recurring image in Dalí’s art, from his early work The Basket of Bread to later public performances such as in 1958 when he gave a lecture in Paris armed with a 12-meter-long baguette. He saw bread as “the elementary basis of continuity” and “sacred subsistence”.
From the late 1920s, Dalí progressively introduced many bizarre or incongruous images into his work which invite symbolic interpretation. While some of these images suggest a straightforward sexual or Freudian interpretation (Dalí read Freud in the 1920s) others (such as locusts, rotting donkeys, and sea urchins) are idiosyncratic and have been variously interpreted. Some commentators have cautioned that Dalí’s own comments on these images are not always reliable.
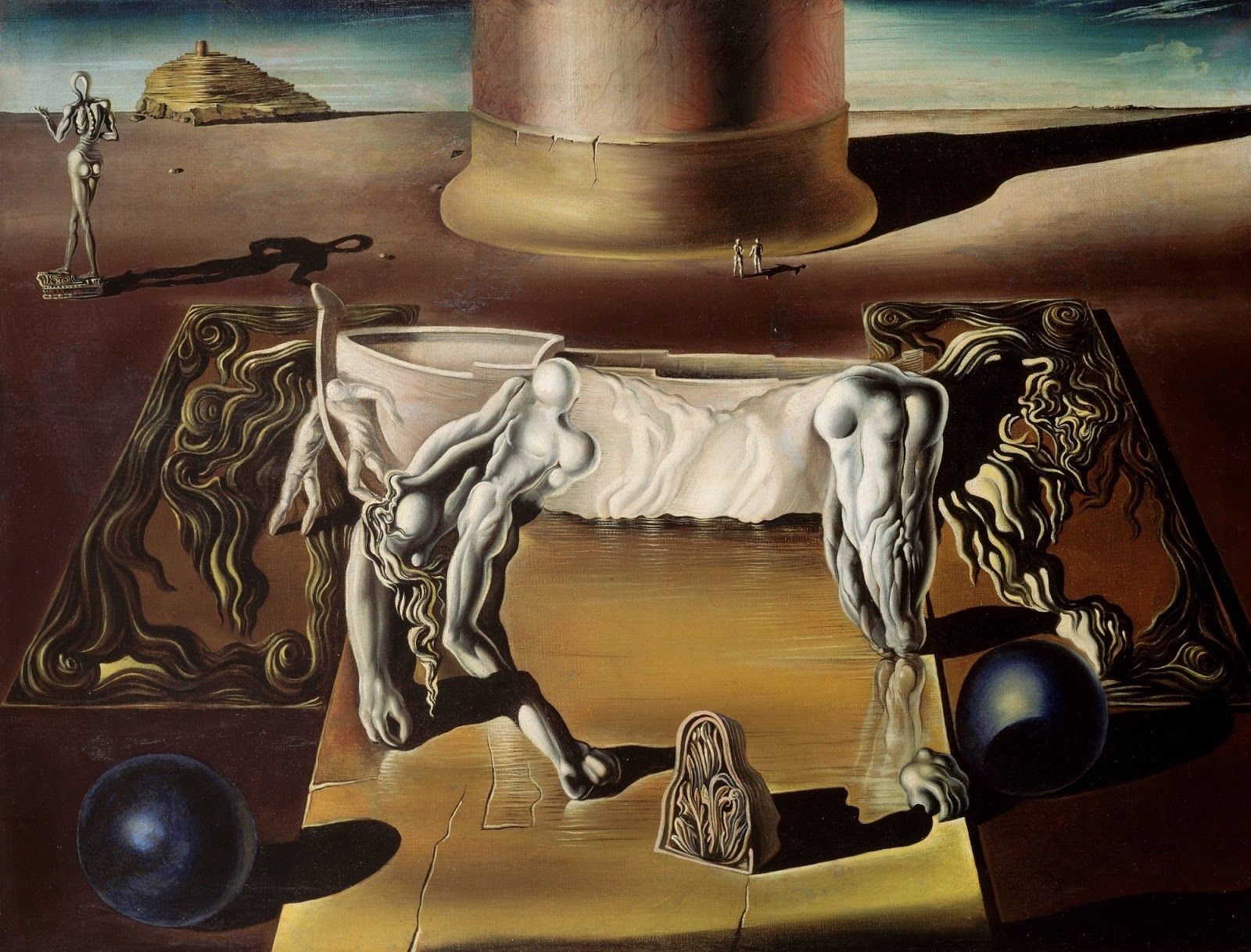

Obsessive themes of eroticism, death, and decay permeate Dalí’s work, reflecting his familiarity with and synthesis of the psychoanalytical theories of his time. Drawing on blatantly autobiographical material and childhood memories, Dalí’s work is rife with often ready-interpreted symbolism, ranging from fetishes and animal imagery to religious symbols.
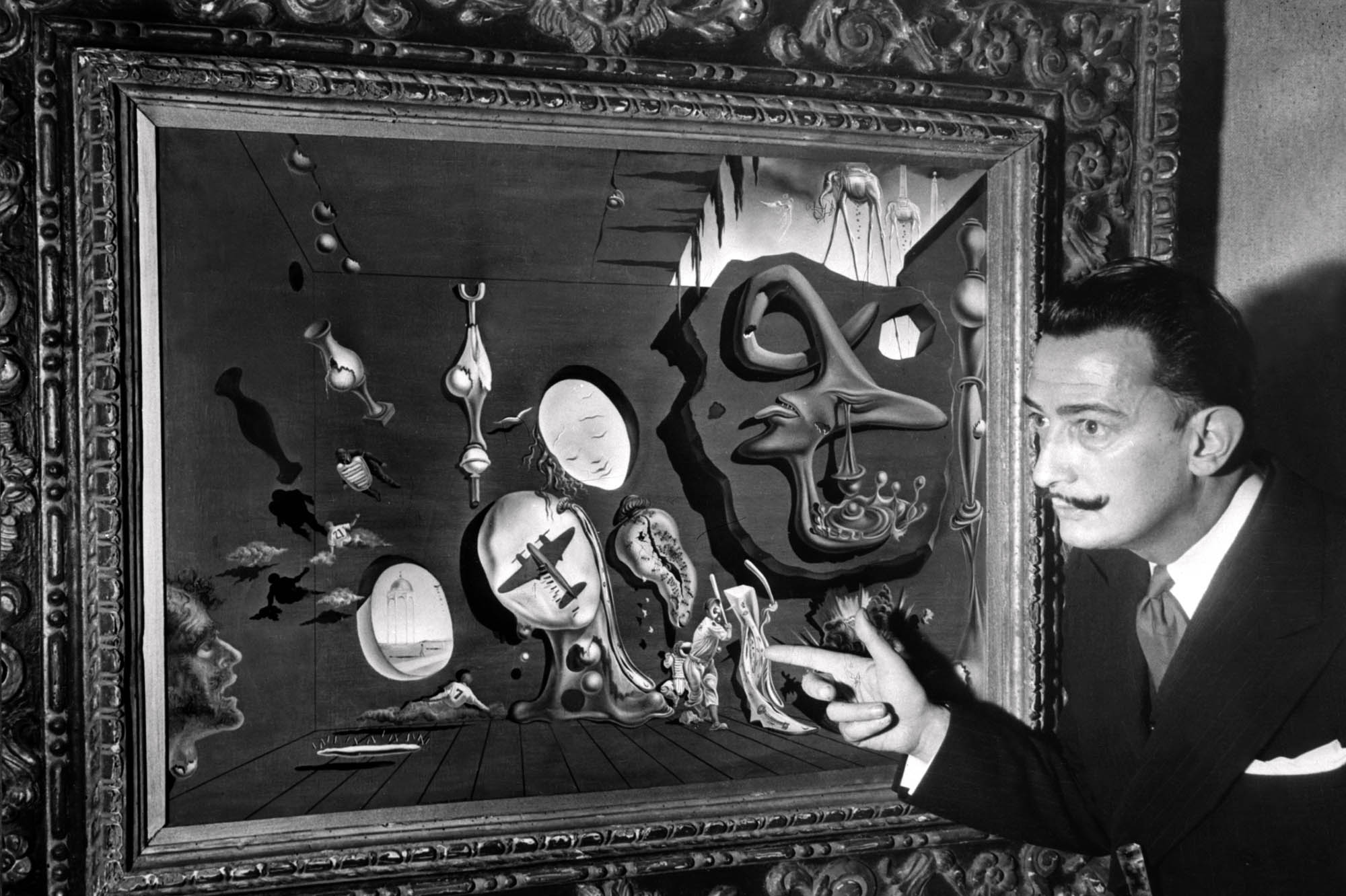

The striking and somewhat bizarre images depicted in his paintings solidified his name in the Surrealist movement and his artwork is still revered by many acclaimed art critics to this day. His ambitious nature ensured that his finely honed technical skills would be extended into a vast number of mediums, as he successfully produced an array of sculptures, drawings, jewellery and furniture.

